Here are the steps to solving a problem involving Newton’s 2nd law.
Step 1: Draw a free body diagram – where possible, sketch a free body diagram to represent:
- the body isolated from other objects
- the forces acting on the body (ignore all internal forces) along the line of motion.
- the direction of acceleration.
Step 2: Write down the equation: $$F_{net}=ma$$
Step 3: Add up the forces on the left-hand side of the equation, making sure that forces acting opposite to the direction of acceleration are subtracted.
Step 4: Solve the equation for the unknown.
For example,
A horizontal force of 12 N is applied to a wooden block of mass 0.60 kg on a rough horizontal surface, and the block accelerates at 4.0 m s-2. What is the magnitude of the frictional force acting on the block?
Step 1: Free-body diagram
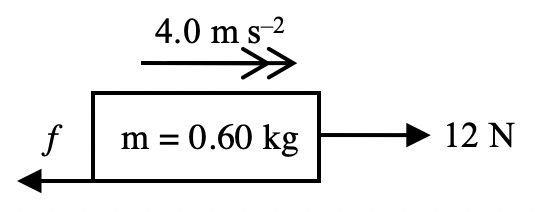
Step 2: Write down the 2nd law equation
By Newton’s 2nd law, $$F_{net}=ma$$
Step 3: Add up the forces making up the net force
$$12 – f = 0.60 (4.0)$$
Step 4: Solve for unknown
$$ f = 12 – 2.4 = 9.6 N$$